Company: Grofers, DE-Shaw, CouponDunia, Amazon, Adobe, Accolite, Snapdeal, Oracle, Kritical Solutions
Question:
Implement a Stack using 2 queue q1 and q2 .
Input :
The first line of the input contains an integer 'T' denoting the number of test cases. Then T test cases follow.
First line of each test case contains an integer Q denoting the number of queries .
A Query Q is of 2 Types
(i) 1 x (a query of this type means pushing 'x' into the stack)
(ii) 2 (a query of this type means to pop element from stack and print the poped element)
The second line of each test case contains Q queries seperated by space.
Output:
The output for each test case will be space separated integers having -1 if the stack is empty else the element poped out from the stack .
You are required to complete the two methods push which take one argument an integer 'x' to be pushed into the stack and pop which returns a integer poped out from the stack.
Constraints:
1<=T<=100
1<=Q<=100
1<=x<=100
Example:
Input
1
5
1 2 1 3 2 1 4 2
Output
3 4
Explanation:
In the first test case for query
1 2 the stack will be {2}
1 3 the stack will be {2 3}
2 poped element will be 3 the stack will be {2}
1 4 the stack will be {2 4}
2 poped element will be 4
Algorithm:
By making pop operation costly:
In push operation, the new element is always enqueued to q1.
Question:
Implement a Stack using 2 queue q1 and q2 .

Input :
The first line of the input contains an integer 'T' denoting the number of test cases. Then T test cases follow.
First line of each test case contains an integer Q denoting the number of queries .
A Query Q is of 2 Types
(i) 1 x (a query of this type means pushing 'x' into the stack)
(ii) 2 (a query of this type means to pop element from stack and print the poped element)
The second line of each test case contains Q queries seperated by space.
Output:
The output for each test case will be space separated integers having -1 if the stack is empty else the element poped out from the stack .
You are required to complete the two methods push which take one argument an integer 'x' to be pushed into the stack and pop which returns a integer poped out from the stack.
Constraints:
1<=T<=100
1<=Q<=100
1<=x<=100
Example:
Input
1
5
1 2 1 3 2 1 4 2
Output
3 4
Explanation:
In the first test case for query
1 2 the stack will be {2}
1 3 the stack will be {2 3}
2 poped element will be 3 the stack will be {2}
1 4 the stack will be {2 4}
2 poped element will be 4
Algorithm:
By making pop operation costly:
In push operation, the new element is always enqueued to q1.
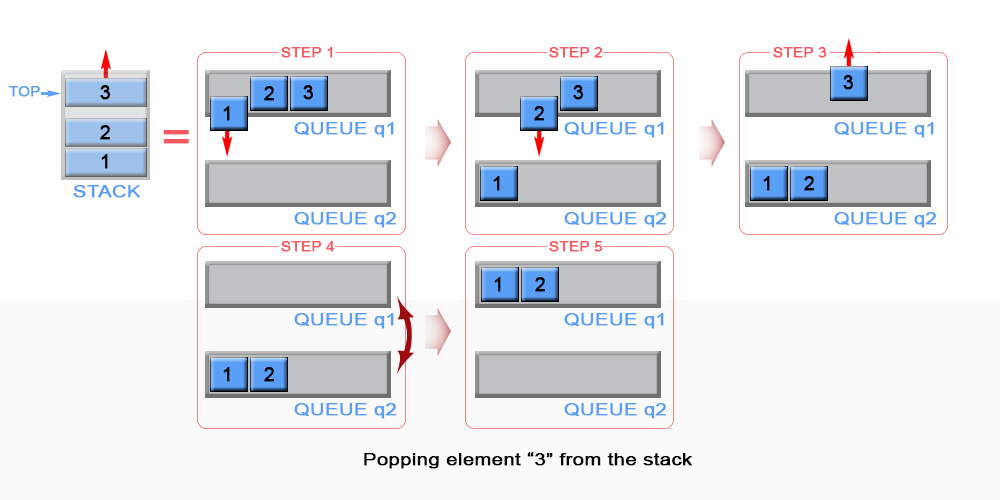
In pop() operation, if q2 is empty then all the elements except the last, are moved to q2.
Finally the last element is dequeued from q1 and returned.push(s, x)
1) Enqueue x to q1 (assuming size of q1 is unlimited).
pop(s)
1) One by one dequeue everything except the last element from q1 and enqueue to q2.
2) Dequeue the last item of q1, the dequeued item is result, store it.
3) Swap the names of q1 and q2
4) Return the item stored in step 2.
// Swapping of names is done to avoid one more movement of all elements
// from q2 to q1.
CODE:
/*
Please note that it's Function problem i.e.
you need to write your solution in the form Function(s) only.
Driver Code to call/invoke your function would be added by GfG's Online Judge.*/
class GfG
{
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
/*The method pop which return the element poped out of the stack*/
int pop()
{
// Your code here
if(q1.isEmpty())
return -1;
else{
while(q1.size()!=1){
q2.add(q1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> q3;
q3=q1;
q1=q2;
q2=q3;
return q2.poll();
}
}
/* The method push to push element into the stack */
void push(int a)
{
// Your code here
q1.add(a);
}
}
EXECUTION TIME: 0.21 secs
Comments
Post a Comment